Brief Summary
Turner syndrome is a condition that only affects the females. It is the result of one missing X chromosome. Turner syndrome causes many variety and developmental problems such as short height, developmental failure of ovaries, and heart defects. There is no treatment for turner syndrome but patients can be administered with ERT and Human growth hormone to help minimize the symptoms.
Inheritance
Frequency
It affects approximately 1 in 2,500 newborn girls around the world, but much more frequent among miscarriages and stillbirths.
The majority of Turner syndrome cases are no inherited. Rather, it is causes by monosomy X, which is a chromosomal aberration that occurs as a random event prior to conception.
TURNER SYNDROME
History of Disease
The disorder was discovered back in 1938, by an endocrinologist named Dr. Henry Turner. This discovery occurred when he was studying 7 girls who had the same abnormal conditions and features. He described the syndrome to manifest poor stature and lack of development of the secondary sex characteristics.
Turner syndrome being linked to the X chromosome happened later on in 1959.
Pathogenesis
Turner syndrome is an effect in the complete or partial absence in one of the female’s X chromosomes. A normal individual would either have two X chromosomes (female) or one X and one Y chromosome (male). Girls who lack an X chromosome are said to have monosomy X Turner syndrome, while those whose X chromosome has a deletion is said to have mosaic Turner syndrome. This absence or deletion is a result of an error during meiosis.
Pathogenesis
Symptoms
1
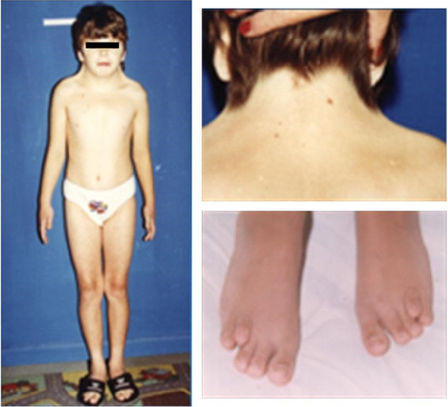
A short neck with a webbed appearance, low hairline at the back of the neck, low-set ears, hands and feet that are swollen or puffy at birth, and soft nails that turn upward
2
Short stature
3
Unnatural puberty (poor breast development)
4
Missing or nonfunctional ovaries
5
Cardiovascular problems
6
Osteoporosis
7
Diabetes
8
Abnormal kidneys (less common)
9
Hypothyroidism
Social Concerns
People living with Turner's syndrome work and think like a normal individual and are also seen as having normal physical and mental health. But challenges for these types of individuals are inevitable. Slow response time, social anxiety and immaturity are some of the behaviors that people living with Turner's syndrome have.
The adjustments and challenges for these individuals might be very difficult for them to cope with and it may cause inappropriate behavior under any circumstances. Social skills and companionship issues in a social environment would also lead to entanglement of the patient's mental health. In accordance with NLD's psycho-social suggestions.
Treatment
Currently, there is no cure for Turner syndrome, however, patients can be administered with the following that can help minimize symptoms. Each patient is different thus, specific therapeutic procedures will differ depending on severity, age, and overall condition. It is also crucial to detect and assess the condition at an early stage.
-
Human growth hormone: Can increase in growth in height.
-
Estrogen replacement therapy (ERT): Enables secondary sexual development such as breasts and widening of the hips. It also provides protection against bone loss.
Expert Directory
References
FOR INFORMATION
FOR IMAGES